Acclimatization - The temporary adaptation of the body to work in the heat that occurs gradually when a person is exposed to it. Acclimatization peaks in most people within four to fourteen days of regular work for about two hours per day in the heat.
Environmental risk factors for heat illness - The working conditions that create the possibility that heat illness could occur, including air temperature, relative humidity, radiant heat from the sun and other sources, conductive heat sources such as the ground, air movement, workload severity and duration, protective clothing and personnel protective equipment worn by employees.
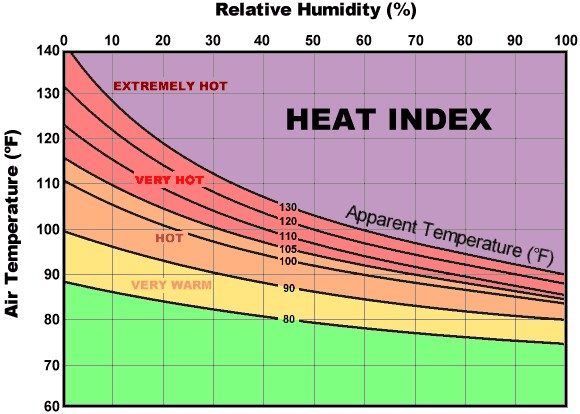
*This heat index chart shows how environmental risk factors can affect someone’s response to heat
Heat illness - A serious medical condition resulting from the body’s inability to cope with a particular heat load, and includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat syncope, and heat stroke. Refer to the chart below on types of illnesses for specific information.
Personal risk factors for heat illness - Factors such as an individual’s age, degree of acclimatization, health, water consumption, alcohol consumption, caffeine consumption, and use of prescription medications that affect the body’s water retention or other physiological responses to heat.
Preventative cool-down rest - A period of time to recover from the heat in order to prevent heat illness.
Shade - The blockage of direct sunlight. Canopies, umbrellas, and other temporary structures or devices may be used to provide shade. One indicator that blockage is sufficient is when objects do not cast a shadow in the area of blocked sunlight. Shade is not adequate when heat in the area of shade defeats the purpose of shade, which is to allow the body to cool. For example, a car sitting in the sun does not provide acceptable shade to a person inside it, unless the car is running with air conditioning. Shade may be provided by any natural or artificial means that does not expose employees to unsafe or unhealthy conditions and that does not deter or discourage access or use.
Temperature - means the dry bulb temperature in degrees Fahrenheit obtainable by using a thermometer to measure the outdoor temperature in an area where there is no shade. While the temperature measurement must be taken in an area with full sunlight, the bulb or sensor of the thermometer should be shielded while taking the measurement, e.g., with the hand or some other object, from direct contact by sunlight.
